Content
Published:
This is an archived release.
Increasing consumption of electricity
Cold weather in November led to the second highest consumption of electric power recorded for this month. At the same time the high prices may have moderated the consumption increase.
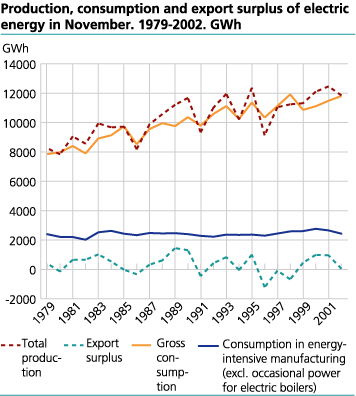
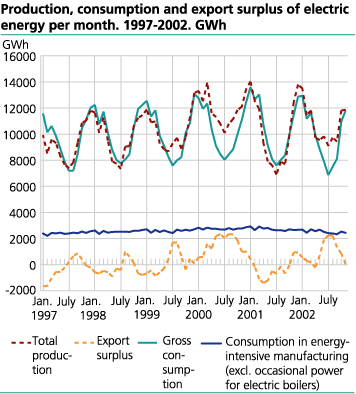
The weather in November has not been this cold since November 1980, and this led to the second highest consumption recorded for this month. The gross consumption of electric energy was 11 804 GWh in November 2002, and this is a 2.8 per cent increase compared with the corresponding month the year before. The temperature in November 2001 was above the normal. The total gross consumption with the exception of power-intensive manufacturing is mainly determined by temperature in short term, and the consumption in this sector increased by 6.1 per cent compared with November 2001.
High prices may have moderated the increase
High prices of electric energy and considerable attention on the prices, supplemented with encouragements for less use of electric energy, may have moderated the increase in the consumption of electricity. The price index for households shows that the total price in November 2002 was 7.6 per cent higher than for the same month the year before. The total price includes the tariff on distribution and taxes in addition to the price on electricity.
Consumption of power-intensive manufacturing decreased
The consumption in power-intensive manufacturing does not depend on temperature, and in November 2002 the consumption of electric energy decreased by 8.3 per cent compared with the corresponding month in 2001. The decrease was mainly caused by less activity in this sector, but can also be explained by high prices on electricity and a switch to the use of other energy bearers. The sale of petroleum products to the industry increased by 77.4 per cent compared with the corresponding month in 2001. The spot price on electricity was on average 31.7 øre/kWh in November 2002, while this price was 17.0 øre/kWh in the same month the year before. The levels of the water reservoirs in November 1996 were approximately the same as in November 2002, and the spot price was on average 22.6 øre/kWh. Higher demand for electric energy can explain some of the difference in the spot prices in 1996 and 2002.
Production down
The production of electric energy was 11 855 GWh in November 2002. This is a 4.8 per cent decrease compared with the corresponding month the year before. In November the precipitation was unusually low. Normally the precipitation in November in the larger areas for trickle of water is in the form of snow and it will fill up the water reservoirs in the end of April. Low precipitation now will lead to expectations of higher value of the water in the future and thereby higher prices today. In November the term prices on average were above the observed spot price. This indicates that a producer could make more profits holding back water for delivery of electricity in the future. This will lead to higher prices today and lower prices in the future than would be the situation with high production today. The import was 596 GWh and the export was 646 GWh in November last year.
See also
Tables:
Contact
-
Magne Holstad
E-mail: magne.holstad@ssb.no
tel.: (+47) 40 90 23 42
-
Ingvild Røstøen Ruen
E-mail: ingvild.ruen@ssb.no
tel.: (+47) 40 81 13 97
-
Tom Jonas Billit
E-mail: tom.billit@ssb.no
tel.: (+47) 40 81 13 45
-
Thomas Aanensen
E-mail: thomas.aanensen@ssb.no
tel.: (+47) 40 90 23 48