Content
Published:
This is an archived release.
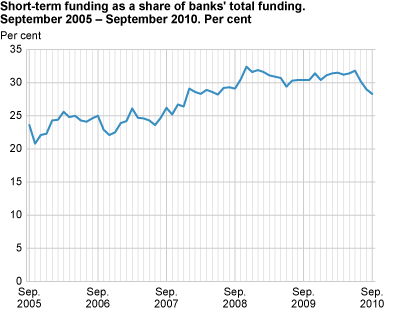
Decrease in short-term funding
Norwegian banks’ short-term funding by end-September amounted to 28.3 per cent of their total funding, down from 29.0 per cent last month. The decrease from last period stems from both certificate debt and interbank loans.
Norwegian banks’ short-term funding is based on the emission of short-term papers (certificates) and interbank loans. The two sources amounted to NOK 833 billion to end-September, or 28.3 per cent of total funding. This is down from 30.4 per cent by end-September last year. The share in June this year was 31.8 per cent; the highest since January 2009.
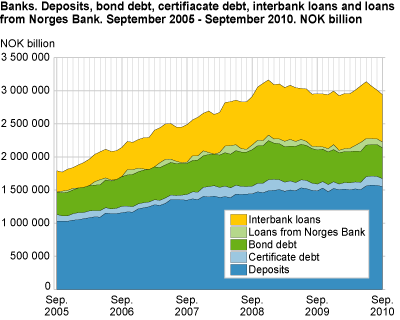
The long-term funding, deposits and bond debt, has naturally increased its share of the banks’ total funding during the same period. Deposits and bond debt aggregated to NOK 2 019 billion to end-September, down from NOK 2 050 billion last month. However, as a share of total funding, the long-term funding has increased from 68.1 to 68.7 per cent from August to September this year. In September last year this share amounted to 67.8 per cent. Besides short and long-term funding sources, loans from Norges Bank constitute the rest of the total funding of the banks.
Decrease in interbank loans
Interbank loans are the major part of the short-term funding sources, and amounted to NOK 716 billion to end-September, or 24.3 per cent of the banks’ total funding. This share is reduced from 27.0 per cent in September last year.
Emission of short-term papers is the other short-term funding source, and has increased from 3.5 to 4.0 per cent of total funding from September last year to September this year. Last month this share was 4.6 per cent. The decrease in the short-term funding from last month stems from both sources, while the decrease from the same point of time last year stems from a reduction in the interbank loans.
Deposits increase as a share of banks’ total funding
Deposits are normally considered as the cheapest and most stable funding source. This is also the biggest funding source, with a share of 52.9 per cent or NOK 1 554 billion to end-September. The share increased from 52.1 per cent by end-August, while it was only 49.0 per cent in May.
Bonds are the other long-term funding source, and have during the last year reduced their share of total funding from 17.4 per cent in September last year to 15.8 per cent in September 2010. Therefore, the increase in long-term funding as a share of total funding stems from deposits.
Fluctuations in F-loans from Norges Bank
F-loans from Norges Bank are a part of the liquidity supply to the banks, and these are loans with collateral in securities at a fixed exchange rate and given terms. The terms for these loans have normally been under a week, but due to the turbulence in the financial markets, Norges Bank enabled loans of up to two years. F-loans amounted to NOK 87 billion to end-September, or 3.0 per cent of the bank’s total funding. This share has fluctuated between 1.1 and 4.6 per cent in the last two years.
Tables
The statistics is now published as Banks and mortgage companies.
Contact
-
Statistics Norway's Information Centre
E-mail: informasjon@ssb.no
tel.: (+47) 21 09 46 42