Content
Published:
This is an archived release.
One third work at inconvenient hours
35 per cent of the employees worked regularly outside ordinary working hours, most in shift work. Employees in hotels and restaurants have the most weekend, evening and night shifts, followed by employees in transport, health and social work and wholesale and retail trade.
All in all the level of shift work is same for the second quarter of 2002 as it was for the second quarter of 2001, according to figures from the second quarter 2002 Labour Force Survey.
|
Employees who regularly work shift by
patterns of working time. 2nd quarter 2001- 2nd quarter 2002. Per cent |
| 2001 | 2002 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Employees, total | 100 | 100 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shift work | 21 | 21 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Where | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Saturday and/or Sunday | 13 | 13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Evening and/or night | 5 | 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| All the combinations | 2 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unspecified | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not shift work, total | 14 | 15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Where | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Saturday and/or Sunday | 7 | 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Evening and/or night | 7 | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The same person may have combinations of several work hour arrangements at the same time, for example both evening and Saturday work. In the rest of this article we will only refer to employees who have any of these working patterns.
22 per cent of females and 19 per cent of males are required by contract to work Saturdays on a regular basis (at least two Saturdays during four weeks). Men and women who are working in the evening make up 15 and 16 per cent [corrected 25.09.02] of the employees, respectively. Night work constitutes 5 per cent for females and 6 per cent for males. Work on Sundays is equally divided between men and women, 12 per cent.
Individuals in regular shift work constitute 26 percent of female and 17 percent [corrected 25.09.02] of male employees.
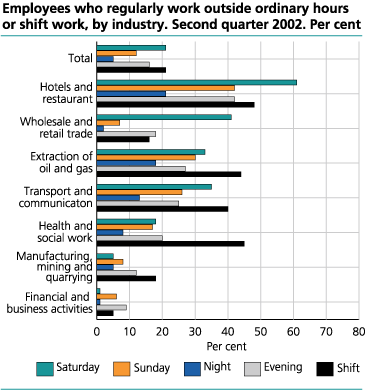
Still most common in the hotel and restaurant industry
Among the largest industries work in shifts is most common in the hotel and restaurant industry, as well as in transportation, health an social services and retail trade. 61 percent of the employees in hotels and restaurants work Saturdays on a regular basis, 42 percent work on Sundays and evenings, and 21 percent work nightshifts. The changes since the 2n d quarter of 2001 may be divided into three main groups. In the hotel and restaurant industry the share of employees working Saturdays, Sundays and evenings was reduced by 5, 7 and 4 percentage points, respectively. The share working nights was about unchanged. The retail industry saw an increase in the use of evening and Sunday shifts by 4 and 2 percentage points, respectively. The use of Saturday and night shifts was nearly unchanged. Health and social services saw only minor change since the 2n d quarter of 2001.
Men employed full time, women employed part time
Industries with an extensive use of irregular working hours may naturally be divided into two categories. In manufacturing and transport it is men who have irregular hours and they are employed full time.
In health and social services and in retail irregular hours are more common among women, and they are to a large extent employed part time.
In the hotel and restaurant industry about the same share of full time and part time employees have irregular hours. But women employed part time work to a larger extent evening and night shifts.
Among the larger occupational groups irregular hours are more common in sales and service occupations together with operators, drivers etc. 42 percent of the employees in sales and service occupations work Saturdays, 19 percent work Sundays, 28 percent work evenings, while 8 percent work nights.
For the most young people, the temporarily employed and part time employed
The portion of temporarily employed persons with irregular working hours has dropped since the 2n d quarter of 2001. But is still greater than for permanently employed persons. They are more likely to work evenings and Saturdays.
Irregular hours are more common among part time employees than full time employees.
Young people 16 - 24 years old are more likely to work irregular hours, in particular in weekends and evenings.
|
Employees who regularly work outside ordinary hours.
2nd quarter 1999-2nd quarter 2002. Per cent |
| 2nd quarter 1999 | 2nd quarter 2000 | 2nd quarter 2001 | 2nd quarter 2002 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saturday | 20 | 21 | 20 | 21 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sunday | 12 | 13 | 12 | 12 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Evening | 16 | 17 | 16 | 16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Night | 5 | 5 | 6 | 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tables:
- Table 1 Employees who regulary work outside ordinary hours or shift work by sex and age. Second quarter 2002. Per cent
- Table 2 Employees who regulary work outside ordinary hours or shift work by sex and industry. Second quarter 2002. Per cent
- Table 3 Employees who regulary work outside ordinary hours or shift work, by occupation. Second quarter 2002. Per cent.
- Table 4 Employees who regulary work outside ordinary hours or shift work, by sex and conditions of appointment. Second quarter 2002. Per cent
The statistics is published with Labour force survey.
Contact
-
Statistics Norway's Information Centre
E-mail: informasjon@ssb.no
tel.: (+47) 21 09 46 42