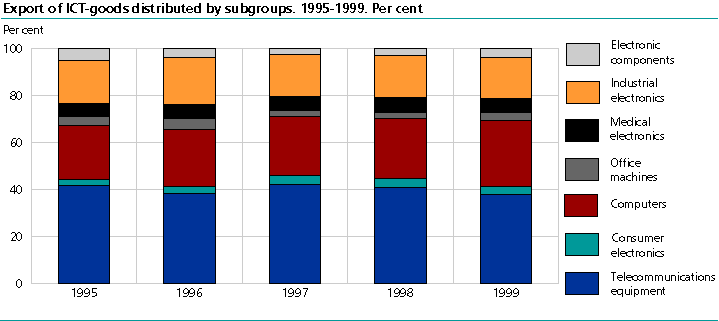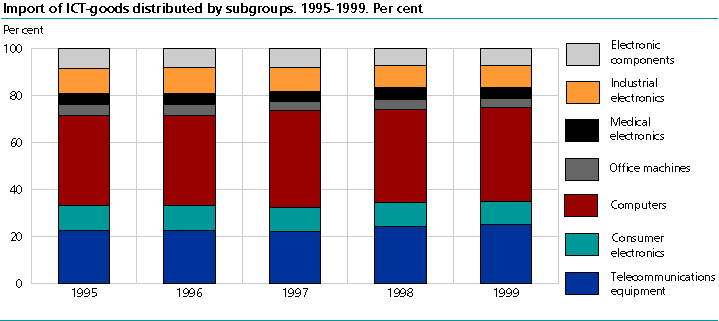Content
Published:
This is an archived release.
Import surplus of ICT goods
External trade in ICT goods showed an import surplus of almost NOK 19 billion. Norwegian exports of ICT goods amounted to almost 40 per cent of imports. Exports and imports of ICT goods grew faster than the rest of external trade from 1995 to 1999.
There is currently no internationally recommended definition of ICT goods. This article is based on a delimitation used in Finland and which will serve as the starting point for Nordic collaboration in the area of ICT statistics. The delimitation includes the product groups telecommunications equipment, consumer electronics, computers, office machines, electro-medical equipment, industrial electronics, electronic components and are explained in greater detail in "About the statistics".
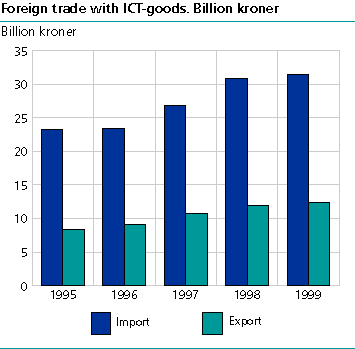
Norway's net import of ICT goods is huge. In 1999 imports were about two and a half times as big as the value of exports. Exports of ICT goods increased in current prices from NOK 8 409 million in 1995 to NOK 12 430 million in 1999, while imports grew from NOK 23 195 million in 1995 to NOK 31 408 million in 1999. In 1999 this resulted in a negative balance of NOK 18 978 million. From 1995 to 1999, the relative trade deficit in such goods fell 3.3 percentage points. The ratio between export and imports of ICT goods in Norwegian external trade was 0.396 in 1999 compared with 0.363 in 1995.
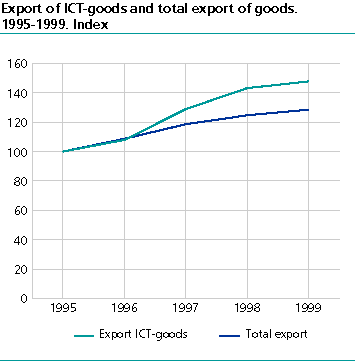
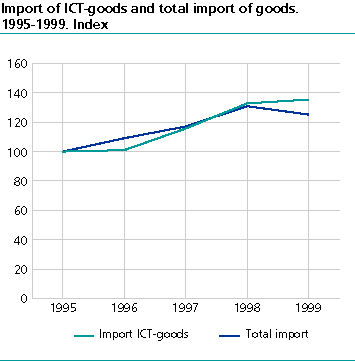
Exports and imports of ICT goods grew faster than the average in the latter half of the 1990s. From 1995 to 1999 Norwegian exports of ICT goods grew by 47.8 per cent in current prices, while imports during the same period increased by 35.4 per cent. From 1995 to 1999 total Norwegian exports grew by 28.5 per cent at the same time as imports rose by 25.2 per cent. Consequently, ICT goods' share of total external trade increased slightly. From 1995 to 1999, ICT goods' share of total exports increased from 5.9 to 6.8 per cent. During the same period the share of ICT goods in relation to imports increased by 11.5 to 12.4 per cent.
In 1999, telecommunications equipment, computers and industrial electronics were the three top export groups, with NOK 4 686, 3 508 and 2 212 million respectively. Telecommunications equipment accounted for about 38 per cent of the value of ICT exports. In 1999, computers made up the largest import group by far, accounting for NOK 12 614 million or about 40 per cent of the value of ICT imports. In second place was telecommunications equipment, with NOK 7 899 million. From 1995 to 1999 the distribution of the product groups within external trade in ICT was relatively stable.
Finland has export surplus
Finland has compiled statistics on the basis of the same delimitations of ICT goods. From 1995 to 1999, Finnish exports of ICT goods surged, pushing the trade surplus in such goods up 54.1 per cent. The ratio between exports and imports in 1999 was 1,660 against 1,119 in 1995. During the same period, Finland increased its exports of ICT goods by 127.2 per cent, while imports grew by 53.1 per cent. In 1999, ICT goods accounted for 22.9 per cent of total Finnish exports, compared with 13.3 per cent in 1995. The corresponding figure for imports was 18.3 per cent in 1999, compared with 16.3 per cent in 1995.
Tables:
Contact
-
Statistics Norway's Information Centre
E-mail: informasjon@ssb.no
tel.: (+47) 21 09 46 42