Norwegian exports of weapons 2010-2014
Lowest exports of arms since 2005
Published:
Export of arms totalled NOK 1.8 billion in 2014. This is 14 per cent less than the previous year and 40 per cent lower than in the peak years of 2008 and 2009 when export values exceeded NOK 3.1 billion.
- Series archive
- Exports of weapons
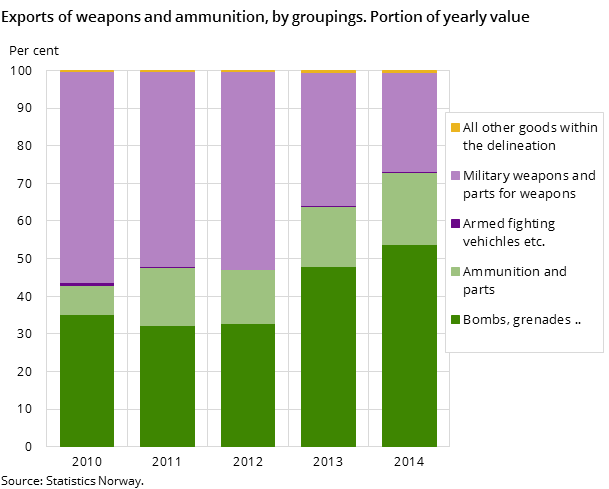
The value of Norwegian exports of military equipment has dropped every year since 2008. A specific decline was seen in the commodity group weapons and parts of weapons, which inter alia includes artillery guns and rockets. The export value has decreased steadily in recent years and ended in 2014 just below NOK 0.5 billion – a third of the 2010 exports when the registered export value for this group came to about NOK 1.5 billion.
Major rise in exports to Luxembourg
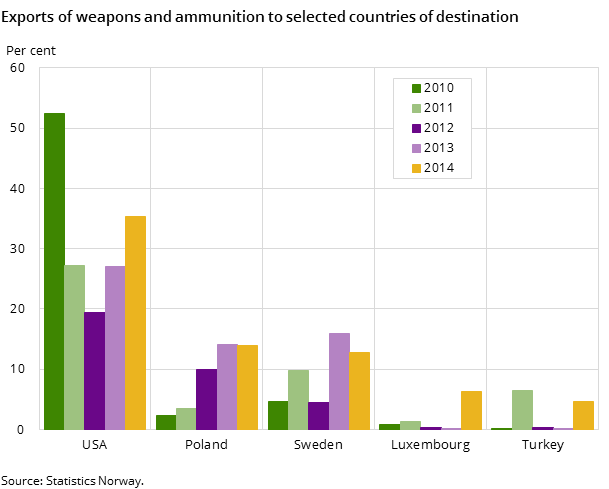
Nearly 80 per cent of the exports of military equipment in 2014 went to NATO countries, totalling NOK 1. 4 billion, of which the USA accounted for 45 per cent. As in 2013, the three largest recipients of Norwegian weapons in 2014, in terms of value, were the USA, Poland and Sweden. Exports to Luxemburg were particularly high and differ from previous years. Luxemburg imported Norwegian weapons for NOK 115 million in 2014 compared to NOK 3 million the year before. Because the export of military equipment often consists of large and expensive deliveries, there is considerable variation in export values from one year to another as well as with respect to which goods are exported.
- Note that the figures presented in this article are based on reported commodity exports of munitions. These do not take into account any incorrect reporting or illegal trade in weapons, which may be substantial in some countries. This makes it difficult to comment on Norway’s actual position in the world market.
Norway continues to be the world's sixth largest exporter of arms
According to the latest figures from the UN database, Comtrade, the world’s total export of military equipment totalled USD 12.9 billion in 2013. This is reported exports of weapons, ammunition and tanks. The Norwegian market share has fallen from 5.4 per cent in the peak year 2008 to 2.8 per cent of all registered exports of weapons in 2013. The USA has been the world's leading exporter for many years and in 2013 accounted for 44 per cent of the world’s total exports of military weapons - amounting to USD 5.7 billion. Exports of weapons from Canada and Italy both accounted for around 6 per cent, while Germany, with an export value of approximately USD 700 million, accounted for roughly 5 per cent of the world’s registered arms sales in 2013. The corresponding figure for South Korea was 3.7 per cent.
Contact
-
Randi Dyrstad
-
Statistics Norway's Information Centre