Content
Published:
This is an archived release.
NOK 250 billion spent on health in 2011
Total health expenditure is estimated at NOK 250 billion in 2011. This corresponds to NOK 50 000 per capita. The government covered 85 per cent of the total health expenditure.
Preliminary estimates indicate that the total health expenditure amounted to about NOK 250 billion in 2011. Of this, current health spending amounted to NOK 241 billion; an increase of 35 per cent in 5 years and 84 per cent in 10 years. The investments in 2011 are estimated to be about NOK 8.4 billion. Investment was higher in the period 2001 to 2009, but completion of some major hospital developments has contributed to lower investments in 2010 and 2011 than in previous years.
Total health expenditure measured as a share of GDP was about 9 per cent in 2011. This share has varied in the last 10 years with economic cycles. In the recession year of 2003, the share was 10 per cent, while it was 8.6 per cent in 2006.
| 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010* | 2011* | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total expenditure on health. NOK million | 150 029 | 159 574 | 168 238 | 176 985 | 186 761 | 201 722 | 218 906 | 230 472 | 237 543 | 249 483 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total expenditure on health in current prices in per cent of GDP | 9.8 | 10.0 | 9.6 | 9.0 | 8.6 | 8.7 | 8.6 | 9.8 | 9.4 | 9.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total expenditure on health in current prices in per cent of GDP Mainland Norway | 12.3 | 12.5 | 12.3 | 12.1 | 11.7 | 11.5 | 11.8 | 12.3 | 12.0 | 11.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total expenditure on healt in current prices per capita | 33 059 | 34 957 | 36 638 | 38 281 | 40 072 | 42 836 | 45 671 | 47 516 | 48 338 | 50 103 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| * Preliminary figures | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Preliminary estimates of health expenditure measured at constant prices show a slight decrease from 2010 to 2011. Our experience is that the preliminary figures underestimate the volume growth. By comparison, the average annual growth rate in the five-year period 2006 to 2011 was 1.1 per cent. When considering only current health expenditure, the average annual volume growth during this period was 1.8 per cent. GDP Mainland Norway rose by 2.9 per cent in the same period.
Volume growth for the different health services varies quite substantially. From 2008 to 2009, which is the last year we have final and detailed estimates for, hospital services had a volume growth of around 3 per cent. This is slightly above the average growth rate for these services in the last 10 years. Long-term care increased by 2.5 per cent from 2008 to 2009, considerably below the average of 4 per cent in the last decade.
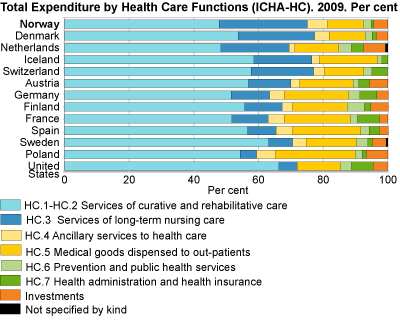
Curative and rehabilitative care services are used the most
Services of curative and rehabilitative care, which include hospital services, GP services, dental care and physiotherapy, and rehabilitation, account for the largest share of the total health expenditure. In Norway, these services accounted for almost 50 per cent of the total health expenditure in 2011, and this share is relatively stable. In comparison, Denmark and Sweden had shares of 54 and 63 per cent of total health expenditure respectively.
The share spent on long-term care varies widely. Norway, Denmark and the Netherlands spend relatively more on these services. Long-term care as a share of the total health expenditure was 27, 24 and 21 per cent respectively in 2009. Sweden differs from the other Scandinavian countries, with a share of 7 per cent. This is mainly explained by the fact that Sweden has not included activities of daily living (ADL), i.e. personal services that are health related, in their estimates. In Poland, medical goods to out-patients accounted for almost a quarter of their health spending in 2009, while the OECD average was 19 per cent (Health at a Glance 2011). In Norway, medical goods accounted for 11 per cent of the total health expenditure in 2009.
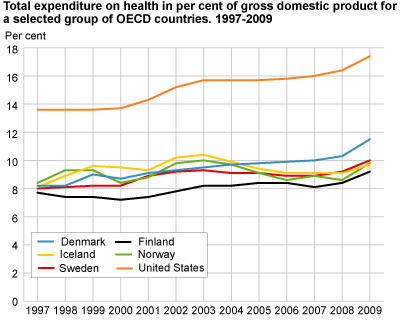
USA has the highest health expenditure
Norway is among the countries that spend the most on health per capita. Only the USA spends more than us. When looking at health expenditure as a share of GDP, final figures for Norway show that we were slightly above the OECD average in 2009, with 9.8 per cent. In the USA, health expenditure as a share of GDP increased from 13.6 per cent in 1997 to 17.4 per cent in 2009. In addition to having the largest share, the USA is also one of the countries that have increased their share the most.
Denmark is the Nordic country with the greatest increase in health expenditure as a share of GDP, with 3.3 percentage points from 1997 to 2009, while Norway’s share in this period increased by 1.4 percentage points.
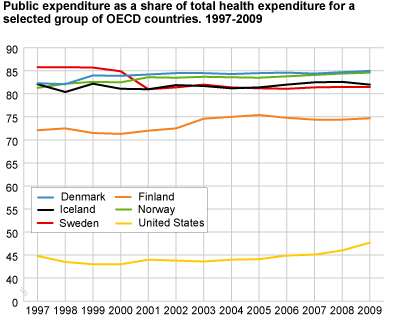
Public sector is main source of health financing
In Norway, public financing of health care has increased steadily from around 81 per cent in 1997 to slightly less than 85 per cent in 2009. In Denmark, public financing covers around 85 per cent of health care, while in Sweden public financing accounts for slightly more than 81 per cent. However, public financing in Sweden was around 86 per cent prior to 2001. Public financing in the USA has increased slightly from 1997, to around 48 per cent in 2009. Their share of private insurance however, at 33 per cent, is substantially higher than in other OECD countries (Health at a Glance 2011).
Tables:
- Table 1 Health expenditure, key figures. 1997-2011
- Table 2 Current expenditure on health, by function of care. 1997-2011. NOK million
- Table 3 Total current expenditure on health by function, distributed by source of funding. 2007. Per cent
- Table 4 Total current expenditure on health by function, distributed by source of funding. 2003. Per cent
- Table 5 Total current expenditure on health by function, distributed by source of funding. 2000. Per cent
- Table 6 Total current expenditure on health by function, distributed by source of funding. 1997. Per cent
- Table 7 Total current expenditure by provider distributed by source of funding. 2007. Per cent
- Table 8 Total current expenditure by provider distributed by source of funding. 2003. Per cent
- Table 9 Total current expenditure by provider distributed by source of funding. 1997. Per cent
Contact
-
Eirik Larsen Lindstrøm
E-mail: eirik.lindstrom@ssb.no
tel.: (+47) 46 78 22 92