Content
About the statistics
Definitions
-
Name and topic
-
Name: Index of household consumption of goods
Topic: Wholesale and retail trade and service activities
-
Next release
-
-
Responsible division
-
Division for National Accounts
-
Definitions of the main concepts and variables
-
Not relevant
-
Standard classifications
-
COICOP (Classification of Individual Consumption by Purpose) is used in the calculation of the index of household consumption goods.
Administrative information
-
Regional level
-
National level only.
-
Frequency and timeliness
-
Monthly, usually published at the end of each month (27th, 28th) (m+1).
-
International reporting
-
Not relevant
-
Microdata
-
Data at micro level, information on population, and catalogues are stored in Oracle databases.
Background
-
Background and purpose
-
The index of household consumption of goods has been published since 1998. The index measures the development of the household consumption of both durable and non-durable goods. Since the definitions in the quarterly national accounts are used in the index of household consumption of goods, it can be interpreted as an indicator of the households’ purchases of goods.
One of the reasons for establishing the index of household consumption goods was changes in the index of retail sales. As of 1996, the index of retail sales was published according to a new classification. After the transition to this new activity classification, the index no longer included sales at petrol stations and sales of motor vehicles. The users demanded a commodity consumption indicator, which included sales of petrol, vehicles and motorcycles, in addition to the index of retail sales. Household consumption of electricity and heating oil was also included in the index computations.
The index of household consumption of goods is compiled by the Division for National Accounts. It is a volume index and is released at the end of each month both as a seasonally adjusted and unadjusted volume figures.
-
Users and applications
-
The index is mainly used by the public sector (ministries, the Central Bank of Norway) and in the financial sector. The index is also used in analysis and research in and outside Statistics Norway.
-
Equal treatment of users
-
No external users have access to the statistics and analyses before they are published and accessible simultaneously for all users on ssb.no at 08.00 am. Prior to this, a minimum of three months' advance notice is given in the Statistics Release Calendar. This is one of Statistics Norway’s key principles for ensuring that all users are treated equally.
-
Coherence with other statistics
-
The index of household consumption goods, which describes the development in household consumption of goods, is published at the same time as the index of retail sales. As opposed to the index of retail sales, the index of household consumption of goods has a wider choice of goods. The calculation of the index is based on information from the index of retail sales plus purchase of cars (initial registration), sales data from petrol stations (petrol and other goods) and consumption of electricity and heating fuels. This may result in deviations in the development of the two indices.
-
Legal authority
-
Not relevant
-
EEA reference
-
Not relevant
Production
-
Population
-
The index of household consumption of goods measures the development in the consumption of all goods (durable and non-durable) offered to households in Norway. The index does not cover household consumption of goods abroad, such as cross-border shopping.
-
Data sources and sampling
-
The most important data source for the index is the index of retail sales broken down by detailed industries. Information on the purchase of vehicles is based on data from the Norwegian Road Federation regarding the initial registration of cars, data from the petroleum statistics are used for information on petrol and heating fuels. Household consumption of electricity uses Statistics Norway’s preliminary estimates on the monthly consumption without extraction of crude petroleum and natural gas and power intensive manufacturing, and is later revised using the final figures of the monthly electricity statistics.
Data from the annual national accounts are used as weights in the calculation of the index of household consumption of goods.
-
Collection of data, editing and estimations
-
The index of household consumption of goods is based on several sources of official statistics and does not have a separate data collection.
Since Statistics Norway gives high priority to timeliness in the release of statistics, the index of household consumption of goods may have to rely on preliminary estimates in some cases. Such estimates will be replaced in subsequent releases.
The same methods and definitions that are used in the quarterly national accounts (QNA) are used in the calculation of the index of household consumption of goods.
The general formula to calculate the consumption of a consumption group in current prices is as follows:
1)
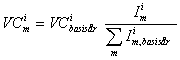
where
VC i m is the consumption group i , in month m, in current prices
VC i basisår is the consumption of a group in the basic year
I i m is the index of retail sales weighted together for consumption (COICOP) group i , in month m.
The first formula defines the consumption in current prices and has been used for all consumption groups where the source has been the index of retail sales. The index for group i will normally be weighting by the detailed activity group indices that are taken from the index of retail sales. The weighting is based on the data for the earnings survey whose starting point is how much each consumption group is purchased in different kind of activity groups (types of shops). The consumption in constant prices is calculated by deflating the COICOP group with the consumers’ price indices for the relevant sub-groups.
2)
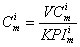
where,
C i m is the consumption of COICOP group i , in month m , in constant prices.
KPI i m is the CPI for consumption group i , in month m
Volume indicators included in the calculations are used in the same way as the index of retail sales. The formula is defined as follows:
3)
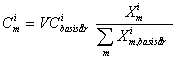
where,
C i m is the consumption of COICOP group i , in month m, in constant prices.
X i m is the volume indicator (e.g. the number of vehicles) for the consumption group i , in month m .
The total consumption of goods in constant prices is defined as the sum of all constant price figures for the different COICOP groups.
4)
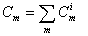
The result from the formula 4 is then used to calculate the index series.
No reconciliation against annual national accounts figures
Constant price figures that form the basis for the index are not reconciled against the annual figures of the national accounts. This means that the sum of the constant price figures for twelve months do not coincide with the annual figures for a given group of commodities. Since the seasonal trend is the most interesting indicator here, we have chosen this solution. If a series has to be reconciled at the end of each year, some of the original seasonal patterns of the indicator can be lost. The level figure for commodity consumption is therefore not published, but only as an index series.
-
Seasonal adjustment
-
The index of household consumption of goods is seasonally adjusted using the same methods as for the quarterly national accounts. It is adjusted both for calendar and normal seasonal effects including corrections for shopping days and the Easter effect.
See "About seasonal adjustment" for more information.
-
Confidentiality
-
Not relevant
Accuracy and reliability
-
Sources of error and uncertainty
-
Not relevant
-
Revision
-
Monthly data of household consumption of goods are changed if the sources are updated with new information. Normally only information about the electricity consumption are changed on a monthly basis. Once in a year, before publishing the index in September, the base year for the calculations is changed. This may lead to revisions in earlier published series.
Even when monthly data for household consumption of goods are not change, the seasonal adjusted figures may be changed as a consequence of updating the series with new monthly figures.
