Content
Published:
This is an archived release.
One in three work outside regular hours
Every third employee works outside regular hours, usually in a shift work arrangement. This kind of work is most common among women and youths. Half of those in part-time employment have this type of work.
According to the Labour Force Survey, 775 000 employees worked outside regular working hours (Monday to Friday from 6 am to 6 pm) in their main job in 2010. This equalled 33 per cent of the total number of employees, and is at the same level as the previous year. The proportion has varied between 33 and 36 per cent in the period from 2001 to 2010. The share of shift workers among those who worked outside regular hours was 71 per cent in 2010.
| 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Employees, total | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ordinary daytime | 65.9 | 65.2 | 64.7 | 65.2 | 64.2 | 65.6 | 65.9 | 66.2 | 67.0 | 66.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outside ordinary daytime | 34.1 | 34.8 | 35.3 | 34.8 | 35.8 | 34.4 | 34.1 | 33.7 | 33.0 | 33.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shift work in the main job | 20.6 | 21.2 | 22.3 | 21.7 | 22.2 | 22.9 | 23.2 | 23.5 | 23.1 | 23.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| All the combinations (Saturday, Sunday, evening and night) | 9.0 | 8.5 | 9.0 | 9.3 | 9.5 | 9.3 | 9.3 | 9.4 | 8.9 | 9.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Saturday, Sunday and evening | 4.9 | 5.4 | 5.7 | 5.4 | 5.4 | 5.8 | 6.0 | 6.1 | 6.6 | 6.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Saturday, Sunday and night | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Saturday and evening | 1.6 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 2.1 | 2.2 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.1 | 2.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Evening and night | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Saturday and Sunday | 1.0 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other combinations of night and/or Saturday/Sunday/evening | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other combinations of Saturday/Sunday/evening | 1.6 | 1.7 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 1.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unspecified | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not shift work, total | 13.5 | 13.6 | 13.0 | 13.1 | 13.6 | 11.5 | 10.9 | 10.2 | 9.9 | 9.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| All the combinations (Saturday, Sunday, evening and night)1 | 2.1 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 2.4 | 2.3 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Saturday, Sunday and evening1 | 2.3 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.1 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 1.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Saturday, evening and night1 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Saturday and evening1 | 2.7 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 2.9 | 2.5 | 2.3 | 2.2 | 2.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Evening and night1 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Saturday and Sunday1 | 1.0 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other combinations of night and/or Saturday/Sunday/evening1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other combinations of Saturday/Sunday/evening1 | 4.4 | 4.4 | 3.8 | 3.7 | 4.0 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | At least one working time is regularly. |
Common in service activities
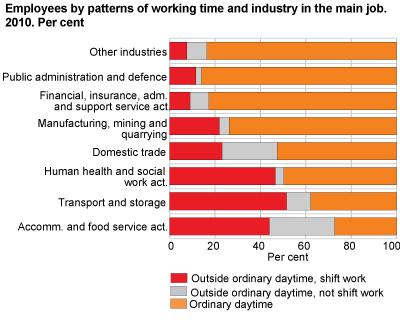
Work outside regular hours is most common in accommodation and food service activities and in transportation and storage, where respectively 73 and 62 per cent had this kind of work in 2010. In human health and social work activities, which employ more people than the two mentioned above combined, half of the employees worked outside regular hours in 2010. Among the employees in domestic trade, 47 per cent had this kind of work. In other service activities, such as public administration and education, work outside regular hours is less common. Fourteen and 10 per cent of the employees in these two industries respectively worked outside regular hours last year. There were only small or no changes in the aforementioned industries from 2009 to 2010.
Most common among women
Last year, the share of women working outside regular hours was 37 per cent - compared to 30 per cent for men. This is approximately the same situation as the year before. The difference reflects the highly gender segregated Norwegian labour market. The main reason that this kind of work is more common among women is that they are highly overrepresented in human health and social work activities. There are many people working in this industry, and work outside regular hours is very common.
There are distinct gender inequalities also with regard to shift work. Among those who worked outside regular hours last year, 74 per cent of the women and 68 per cent of the men had a shift work arrangement. This is also related to the female dominated human health and social work activities. While 93 per cent of the employees in human health and social work activities with work outside regular hours had a shift work arrangement in 2010, the corresponding share for the rest of the industries was 61 per cent.
Almost half of all youths work outside regular hours
Forty-eight per cent of the employees aged 15-29 worked outside regular hours in 2010. Work outside regular hours can be a practical way of combining work and studies for young people. It is particularly the combination of Saturday and evening work that is more common among employees of this age than among the rest. The youngest employees differ from the rest also with regard to the frequency of shift work arrangements. These kinds of arrangements are less common among employees aged 15-29 with work outside regular hours (63 per cent) than among those aged 30-54 (77 per cent).
Distinct inequalities between those in part-time and full-time employment
While 51 per cent of those in part-time employment worked outside regular hours last year, the corresponding share among those in full-time employment was 27 per cent. Both women and youths are overrepresented among the part-time workers. Viewing the full-time and the part-time employees separately, there are only small differences between men and women with regard to the proportions working outside regular hours. Among the full-time employees, the shares were 28 and 26 per cent for women and men respectively - and among the part-time employees the corresponding shares were 51 and 50 per cent. Thus, work outside regular hours is about as common among part-time working men as among part-time working women, but the latter group is far more numerous. The combination of Saturday, Sunday and evening work in a shift work arrangement is more common among part-time employees than among full-time employees.
Multiple working time arrangementsAn individual may have multiple working time arrangements, e.g. both evening and Saturday work. In this article we look at employees with any of these working time arrangements. Hence, we have counted (in table 4-8) the number of different working time arrangements for each employee, not the number of employees. As a result, the total number of working time arrangements is higher than the total number of employees. |
Tables
Employees
- Table 1. Employees by patterns of working time, sex and age. In the main job. 1 000 and per cent. 2010
- Table 2. Employees by patterns of working time, working hours and conditions of appointment. In the main job. Per cent. 2010
- Table 3. Employees by patterns of working time and industry. In the main job. Per cent. 2010
Patterns of working time
- Table 4. Patterns of working time by sex, age and regularity. In the main job. 1 000. 2010
- Table 5. Regularly patterns of working time by sex and industry. In the main job. 1 000 and per cent of employees. 2010
- Table 6. Regularly patterns of working time by working hours and age. In the main job. 1 000 and per cent of employees. 2010
- Table 7. Regularly patterns of working time by working hours and sex. In the main job. 1 000 and per cent. 2010 of employees.
- Table 8. Regularly patterns of working time by conditons of appointment and sex. In the main job. 1 000 and per cent of employees. 2010
The statistics is published with Labour force survey.
Contact
-
Statistics Norway's Information Centre
E-mail: informasjon@ssb.no
tel.: (+47) 21 09 46 42